MongoDB Quick-Start
Edited March 1, 2022 by Leon Hwang
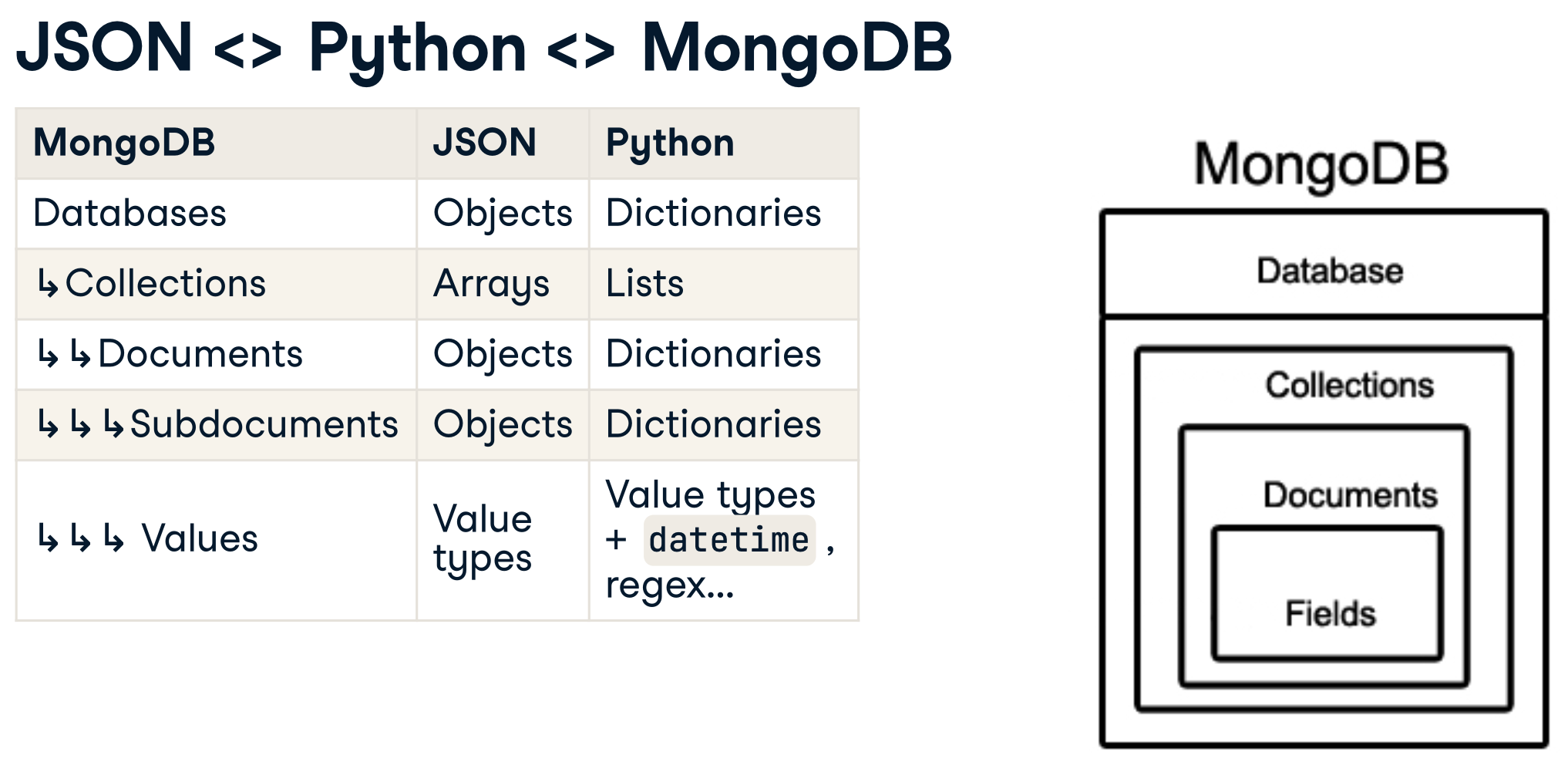
MongoDB is a document-oriented database and one of the most popular NoSQL databases. It uses JSON-like documents. MongoDB offers both local and cloud-hosted options, called MongoDB Atlas.
A record in MongoDB is a document which is composed of field-value pairs similar to JSON objects. MongoDB stores documents in collections that is equivalent to tables in relational databases.
Basic Commands
MongoDB supports a rich query language to support CRUD operations, data aggregation, text search, as well as geospatial queries. MondoDB shell supports the javascript style syntax. Here are some basic commands. You can find more MongoDB methods here.
Connect MongoDB Shell
# connects to mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017 by default
mongo
# connects to a specific MongoDB server
mongo --host <host> --port <port> -u <user> -p <pwd>
mongo "mongodb://192.168.1.1:27017"
# connects to MongoDB Atlas
mongo "mongodb+srv://cluster-name.abcde.mongodb.net/<dbname>" --username <username>
Databases and Collections
// prints the current database
show dbs
// switch database
use <database_name>
// removes the collection and its index definitions
db.coll.drop()
db.dropDatabase()
// show collections
show collection
// create collection with a $jsonschema
db.createCollection("contacts", {
validator: {$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: "object",
required: ["phone"],
properties: {
phone: {
bsonType: "string",
description: "must be a string and is required"
},
email: {
bsonType: "string",
pattern: "@mongodb\.com$",
description: "must be a string and match the regular expression pattern"
},
status: {
enum: [ "Unknown", "Incomplete" ],
description: "can only be one of the enum values"
}
}
}}
})
// other collection functions
db.coll.stats()
db.coll.storageSize()
db.coll.totalIndexSize()
db.coll.totalSize()
db.coll.validate({full: true})
// rename collection and drop the target collection if exists
db.coll.renameCollection("new_coll", true)
CRUD
CREATE
// insert a single record
db.coll.insertOne({name: "Max"})
// ordered bulk insert
db.coll.insert([{name: "Max"}, {name:"Alex"}])
// unordered bulk insert
db.coll.insert([{name: "Max"}, {name:"Alex"}], {ordered: false})
// insert date
db.coll.insert({date: ISODate()})
// insert with writeConcern
db.coll.insert({name: "Max"}, {"writeConcern": {"w": "majority", "wtimeout": 5000}})
READ
// returns a single document
db.coll.findOne()
// returns a cursor - show 20 results - "it" to display more
db.coll.find()
// prettify results
db.coll.find().pretty()
// implicit logical "AND"
db.coll.find({name: "Max", age: 32})
// datetime support
db.coll.find({date: ISODate("2020-09-25T13:57:17.180Z")})
// or "queryPlanner" or "allPlansExecution"
db.coll.find({name: "Max", age: 32}).explain("executionStats")
// return distinct names
db.coll.distinct("name")
// count estimation based on collection metadata
db.coll.count({age: 32})
// count estimation based on collection metadata
db.coll.estimatedDocumentCount()
// alias for an aggregation pipeline - accurate count
db.coll.countDocuments({age: 32})
// comparison
db.coll.find({"year": {$gt: 1970}})
db.coll.find({"year": {$gte: 1970}})
db.coll.find({"year": {$lt: 1970}})
db.coll.find({"year": {$lte: 1970}})
db.coll.find({"year": {$ne: 1970}})
db.coll.find({"year": {$in: [1958, 1959]}})
db.coll.find({"year": {$nin: [1958, 1959]}})
// logical
db.coll.find({name:{$not: {$eq: "Max"}}})
db.coll.find({$or: [{"year" : 1958}, {"year" : 1959}]})
db.coll.find({$nor: [{price: 1.99}, {sale: true}]})
db.coll.find({
$and: [
{$or: [{qty: {$lt :10}}, {qty :{$gt: 50}}]},
{$or: [{sale: true}, {price: {$lt: 5 }}]}
]
})
// element
db.coll.find({name: {$exists: true}})
db.coll.find({"zipCode": {$type: 2 }})
db.coll.find({"zipCode": {$type: "string"}})
// aggregation pipeline
db.coll.aggregate([
{$match: {status: "A"}},
{$group: {_id: "$cust_id", total: {$sum: "$amount"}}},
{$sort: {total: -1}}
])
// text search with a "text" index
db.coll.find(
{$text: {$search: "cake"}}, {score: {$meta: "textScore"}}).sort(
{score: {$meta: "textScore"}}
)
// regular expression
db.coll.find({name: /^Max/})
db.coll.find({name: /^Max$/i})
// array
db.coll.find({tags: {$all: ["Realm", "Charts"]}})
// impossible to index - prefer storing the size of the array & update it
db.coll.find({field: {$size: 2}})
// element level matching
db.coll.find({results: {$elemMatch: {product: "xyz", score: {$gte: 8}}}})
// projections - actors + _id
db.coll.find({"x": 1}, {"actors": 1})
// projections - actors
db.coll.find({"x": 1}, {"actors": 1, "_id": 0})
// projections - all but "actors" and "summary"
db.coll.find({"x": 1}, {"actors": 0, "summary": 0}) //
// sort, skip, limit
db.coll.find({}).sort({"year": 1, "rating": -1}).skip(10).limit(3)
// read concern
db.coll.find().readConcern("majority")
UPDATE
// replaces the entire document
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {"year": 2016})
// set specific fields
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$set: {"year": 2016, name: "Max"}})
// unset specific fields
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$unset: {"year": 1}})
// rename fields
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$rename: {"year": "date"} })
// arithmetic operations
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$inc: {"year": 5}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$mul: {price: NumberDecimal("1.25"), qty: 2}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$min: {"imdb": 5}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$max: {"imdb": 8}})
// datetime operations
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$currentDate: {"lastModified": true}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$currentDate: {"lastModified": {$type: "timestamp"}}})
// array
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$push :{"array": 1}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$pull :{"array": 1}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$addToSet :{"array": 2}})
// last element
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$pop: {"array": 1}})
// first element
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$pop: {"array": -1}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$pullAll: {"array" :[3, 4, 5]}})
db.coll.update({"_id": 1}, {$push: {scores: {$each: [90, 92, 85]}}})
db.coll.updateOne({"_id": 1, "grades": 80}, {$set: {"grades.$": 82}})
db.coll.updateMany({}, {$inc: {"grades.$[]": 10}})
db.coll.update(
{},
{$set: {"grades.$[element]": 100}},
{multi: true, arrayFilters: [{"element": {$gte: 100}}]}
)
// update many
db.coll.update({"year": 1999}, {$set: {"decade": "90's"}}, {"multi":true})
db.coll.updateMany({"year": 1999}, {$set: {"decade": "90's"}})
// find one and update
db.coll.findOneAndUpdate(
{"name": "Max"},
{$inc: {"points": 5}}, {returnNewDocument: true}
)
// upsert
db.coll.update(
{"_id": 1},
{$set: {item: "apple"}, $setOnInsert: {defaultQty: 100}}, {upsert: true}
)
// replace
db.coll.replaceOne({"name": "Max"}, {"firstname": "Maxime", "surname": "Beugnet"})
// save
db.coll.save({"item": "book", "qty": 40})
// write concern
db.coll.update({}, {$set: {"x": 1}}, {"writeConcern": {"w": "majority", "wtimeout": 5000}})
DELETE
db.coll.remove({name: "Max"})
db.coll.remove({name: "Max"}, {justOne: true})
// deletes all the docs but not the collection itself and its index definitions
db.coll.remove({})
db.coll.remove({name: "Max"}, {"writeConcern": {"w": "majority", "wtimeout": 5000}})
db.coll.findOneAndDelete({"name": "Max"})
Using MongoDB with Python
While there are various python libraries for MongoDB, pymongo is one of the most popular one.
Connection
from pymongo import MongoClient
# default host and port
client = MongoClient()
# specify host and port
client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
# use URI
client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
Getting a Database
# access db using attribute style
db = client.test_database
# the following won't work with attribute style because of `-`
# access db using dictionary style
db = client['test-database']
Getting a Collection
# list all of the collections in the database
db.list_collection_names()
# access db using attribute style
collection = db.test_collection
# the following won't work with attribute style because of `-`
# access db using dictionary style
collection = db['test-collection']
CRUD
CREATE
import datetime
# insert single document
post = {
"author": "Mike",
"text": "My first blog post!",
"tags": ["mongodb", "python", "pymongo"],
# pymongo converts native python types to/from the appropriate BSON types
"date": datetime.datetime.utcnow()}
# posts is the collection
posts.insert_one(post)
# insert multiple documents
bulk_post = [{
"author": "Mike",
"text": "My first blog post!",
"tags": ["mongodb", "python", "pymongo"],
"date": datetime.datetime.utcnow()}, {
"author": "Bob",
"text": "I love MongoDB",
"tags": ["mongodb"],
"date": datetime.datetime.utcnow()}]
posts.insert_many([post])
READ
# returns a single document matching a query
# None if no match is found
posts.find_one()
posts.find_one({"author": "Mike"})
# `_id` is a special value in ObjectId
# if post_id is already an ObjectId
posts.find_one({"_id": post_id})
# if post_id is not an ObjectId
posts.find_one({"_id": ObjectId(post_id)})
# `_id` is not a string
posts.find_one({"_id": str(post_id)}) # No result
# returns multiple documents
# `find` returns a cursor instance
for post in posts.find({"author": "Mike"}):
print(post)
# counting
posts.count_documents({})
posts.count_documents({"author": "Mike"})
# value in a range: `$in`
posts.count_documents({"author": {"$in": ["Mike", "Bob"]}})
# not equal: `$ne`
posts.count_documents({"author": {"$ne": "Mike"}})
# advanced queries
# `$lt` means less than
for post in posts.find(
{"date": {"$lt": datetime.datetime(2009, 11, 12, 12)}}
).sort("author"):
print(post)
UPDATE
# update one document
result = posts.update_one(
{"author": "Mike"},
{"text": "Hellp PyMongo!"})
print(result.matched_count) # returns 1
print(result.modified_count) # returns 1
# returns the original version of the document
result = posts.find_one_and_update(
{"author": "Mike"},
{"text": "Hellp PyMongo!"})
# returns the updated version of the document
result = posts.find_one_and_update(
{"author": "Mike"},
{"text": "Hellp PyMongo!"},
return_document=ReturnDocument.AFTER)
# update if found; otherwise, insert a new document
result = posts.update_one(
{"author": "Mike"},
{"text": "Hellp PyMongo!"},
upsert=True)
# update all documents that `author` is `Mike`
result = posts.update_many(
{"author": "Mike"},
{"text": "Hellp PyMongo!"})
DELETE
# delete one document
posts.delete_one({"author": "Mike"})
# delete all documents that `author` is `Mike`
posts.delete_many({"author": "Mike"})
Aggregation
Aggregation operates on multiple documents and returns computed results such as the total, average, min/max values, etc.. For example, the following code filters the pizza order documents to pizzas with a size of medium, groups them by pizza name, and calculate the total order quantity for each pizza name.
// orders collection
db.orders.insertMany( [
{ _id: 0, name: "Pepperoni", size: "small", price: 19,
quantity: 10, date: ISODate( "2021-03-13T08:14:30Z" ) },
{ _id: 1, name: "Pepperoni", size: "medium", price: 20,
quantity: 20, date : ISODate( "2021-03-13T09:13:24Z" ) },
{ _id: 2, name: "Pepperoni", size: "large", price: 21,
quantity: 30, date : ISODate( "2021-03-17T09:22:12Z" ) },
{ _id: 3, name: "Cheese", size: "small", price: 12,
quantity: 15, date : ISODate( "2021-03-13T11:21:39.736Z" ) },
{ _id: 4, name: "Cheese", size: "medium", price: 13,
quantity:50, date : ISODate( "2022-01-12T21:23:13.331Z" ) },
{ _id: 5, name: "Cheese", size: "large", price: 14,
quantity: 10, date : ISODate( "2022-01-12T05:08:13Z" ) },
{ _id: 6, name: "Vegan", size: "small", price: 17,
quantity: 10, date : ISODate( "2021-01-13T05:08:13Z" ) },
{ _id: 7, name: "Vegan", size: "medium", price: 18,
quantity: 10, date : ISODate( "2021-01-13T05:10:13Z" ) }
] )
db.orders.aggregate( [
// Stage 1: Filter pizza order documents by pizza size
{$match: { size: "medium" }},
// Stage 2: Group remaining documents by pizza name and calculate total quantity
{$group: { _id: "$name", totalQuantity: { $sum: "$quantity" }}}])
// Example output
[
{ _id: 'Cheese', totalQuantity: 50 },
{ _id: 'Vegan', totalQuantity: 10 },
{ _id: 'Pepperoni', totalQuantity: 20 }
]
The following example calculates the total pizza order value and average order quantity between two dates
db.orders.aggregate( [
// Stage 1: Filter pizza order documents by date range
{$match: {
"date": { $gte: new ISODate( "2020-01-30" ), $lt: new ISODate( "2022-01-30" ) }
}},
// Stage 2: Group remaining documents by date and calculate results
{$group: {
_id: { $dateToString: { format: "%Y-%m-%d", date: "$date" } },
totalOrderValue: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } },
averageOrderQuantity: { $avg: "$quantity" }
}},
// Stage 3: Sort documents by totalOrderValue in descending order
{$sort: { totalOrderValue: -1 }}
] )
// Example ouptut
[
{ _id: '2022-01-12', totalOrderValue: 790, averageOrderQuantity: 30 },
{ _id: '2021-03-13', totalOrderValue: 770, averageOrderQuantity: 15 },
{ _id: '2021-03-17', totalOrderValue: 630, averageOrderQuantity: 30 },
{ _id: '2021-01-13', totalOrderValue: 350, averageOrderQuantity: 10 }
]
Using Aggregation with Python
# Aggregate
cursor = db.laureates.aggregate([
{"$match": {"bornCountry": "USA"}},
{"$project": {"prizes.year": 1}},
{"$limit": 3}
) ])
# Access the aggregation result via the cursor
for doc in cursor:
print(doc["prizes"])
# Example output
[{'year': '1923'}]
[{'year': '1927'}]
[{'year': '1936'}]
# Adding sort and skip
from collections import OrderedDict
list(db.laureates.aggregate([
{"$match": {"bornCountry": "USA"}},
{"$project": {"prizes.year": 1, "_id": 0}},
{"$sort": OrderedDict([("prizes.year", 1)])},
{"$skip": 1},
{"$limit": 3}
]))
# Example output
[{'prizes': [{'year': '1912'}]},
{'prizes': [{'year': '1914'}]},
{'prizes': [{'year': '1919'}]}]
# Multi-parameter operator expression
db.laureates.aggregate([
{"$project": {"solo_winner": {"$in": ["1", "$prizes.share"]}}}
]).next()
# Example output
{'_id': ObjectId('5bd3a610053b1704219e19d4'), 'solo_winner': True}
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MongoDB
- https://www.mongodb.com/developer/quickstart/cheat-sheet/
- https://app.datacamp.com/learn/courses/introduction-to-using-mongodb-for-data-science-with-python
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/crud/
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/method/
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/operator/
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/aggregation/
- https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/operator/aggregation-pipeline/
- https://pymongo.readthedocs.io/en/stable/tutorial.html
- https://pymongo.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/pymongo/collection.html