AWS DevOps
Edited March 2, 2022 by Adrian Woo
AWS provides a set of developer tools to automatically build, test and deploy applications to AWS or an on-premises environment.
Continous Integration/Continous Delivery (CI/CD) tools
AWS Codepipeline:
Below is an example of how to setup CI/CD process in AWS.
Figure 1: AWS Code Services (Kivanc 2019)
AWS CodeCommit
This allows engineers to collaboratively develop code in software developments without the hassle of maintaining a source control system and worrying about scalability. It supports the standard functionality of Git.
Benefits:
- Fully managed - Fully managed version control service that tracks changes in any set of files in Git-based repositories
- Highly scalable – can scale up to handle a large amount of files
- Easy adoption – can easily migrate from any other git-based repository to CodeCommit
Getting started:
- Create a CodeCommit repository
- Add files to the repository
- Browse the contents of your repository
- Create and collaborate on a pull request
Detailed Guide: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codecommit/latest/userguide/getting-started-cc.html
AWS CodeBuild
A fully managed continuous integration service that compiles source code, runs tests, and puts them into packages that are ready to deploy. CodeBuild automatically creates artifacts to build the environment.
Benefits:
- Fully managed by AWS – no software installation required
- Automatically scale – it scales up and down automatically to meet build demand
- Extensible – allows developers to build their own customized environment
Getting started:
- Define a build environment that represents a combination of an operating system, programming language runtime, and tools that CodeBuild uses to run a build
- CodeBuild uses the parameters in step 1 to build the environment
- Once the built environment is setup, CodeBuild downloads source codes into the build environment and runs the source codes
Detailed Guide: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codebuild/latest/userguide/getting-started.html
AWS CodeDeploy
Fully managed deployment service that automates application deployments to AWS EC2 instances, on-premises servers, AWS lambda functions, or AWS ECS services. CodeDeploy supports a wide variety of application content such as code, AWS lambda functions, web files, executables, packages, scripts, and multimedia files.
Benefits:
- Automated deployment – deploy to development, test, and production environments seamlessly
- Minimize downtime – maximize application uptime during deployment. It monitors applications' health and allows rollback whenever there are errors.
- Easy to adopt – It is language-agnostic that provides the same experience when deploying to Amazon EC2, AWS lambda, or any other platform. It can easily be integrated with the existing software release process.
Steps to deploy on an AWS EC2/on-premise computing platform:
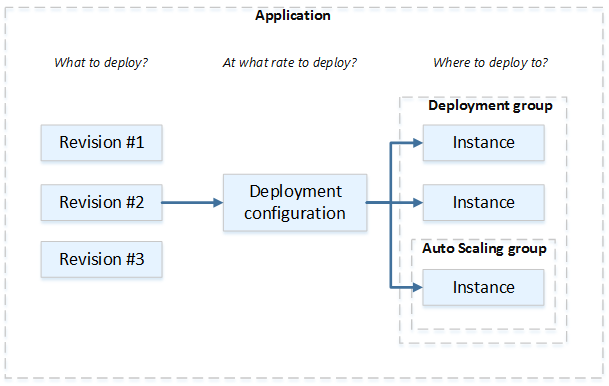
Figure 2: AWS CodeDeploy components (Deployments on an EC2/On-Premises Compute Platform)
- Create an application with a unique name
- Setup a deployment group which is a set of individual instances where CodeDeploy would deploy applications. The deployment group has the following settings:
Deployment type:
- In-place deployment: application on each instance is stopped. Then, the latest version application is installed, validated, and deployed
- Blue/green deployment: instances in the deployment group are replaced by a new set of instances. Then, the latest version applications are installed on the new set of instances. Finally, the old instances are terminated. Tags to instances for deployment:
- CodeDeploy deploys only to the instances that have at least one of the specified tags applied or to instances that meet the criteria for each of the tag groups Other settings:
- Amazon SNS notifications – send a notification when deployment job succeeded or failed
- Alarm-based deployment management – monitor deployment job when specific metrics exceed or fall below the threshold
- Automatic deployment rollbacks – automatically rollback to previous revision when deployment fails
- Specify deployment configuration to indicate how many instances are deployed simultaneously and to describe the success or failure condition of the deployment job. Upload application revision, and any deployment files and scripts to S3 or GitHub. Application specification files must be included to describe copied files destinations and executable scripts during deployment.
- Monitor results
- To redeploy a revision: bundle revised source content, deployment scripts, and the Application specification file into a new revision. Then, upload the revision to the Amazon S3 bucket or GitHub repository.
Detailed guide: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy/latest/userguide/deployment-steps-server.html
Tutorial video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jcR9iIWdU7E
AWS Codepipeline:
Codepipeline is a continuous delivery service that automatically builds, tests, and deploys applications on AWS cloud. It automates the release process from end to end through build, test, and deployment. Developers can implement manual approval at any stage of the pipeline to control where the application is built and deployed. DevOps engineers have full visibilities of the DevOps pipelines in real-time to see alerts, failed actions, and details about the revisions of the code.
Tutorial video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OnI_nXa5yH4
Best practices and use cases: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/latest/userguide/best-practices.html
Reference:
Presentation that explains DevOps and AWS CodeStar Example: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pIaB7wSSReU&t=1s
CI/CD tutorial in AWS: https://medium.com/@emrahkivanc/aws-code-services-easy-as-pie-2aa7b7cc6c37
Complete CI/CD guide in AWS: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/devops/complete-ci-cd-with-aws-codecommit-aws-codebuild-aws-codedeploy-and-aws-codepipeline/
AWS CodeBuild Concept: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codebuild/latest/userguide/concepts.html